Secretarial Audit is an important method for all organizations. It is a part of total compliance management in an organization. It is an effective tool when it comes to corporate compliance management. In this blog we will discuss in detail about the secretarial audit in India, its process and benefits.
What is the requirement of secretarial audit in India?
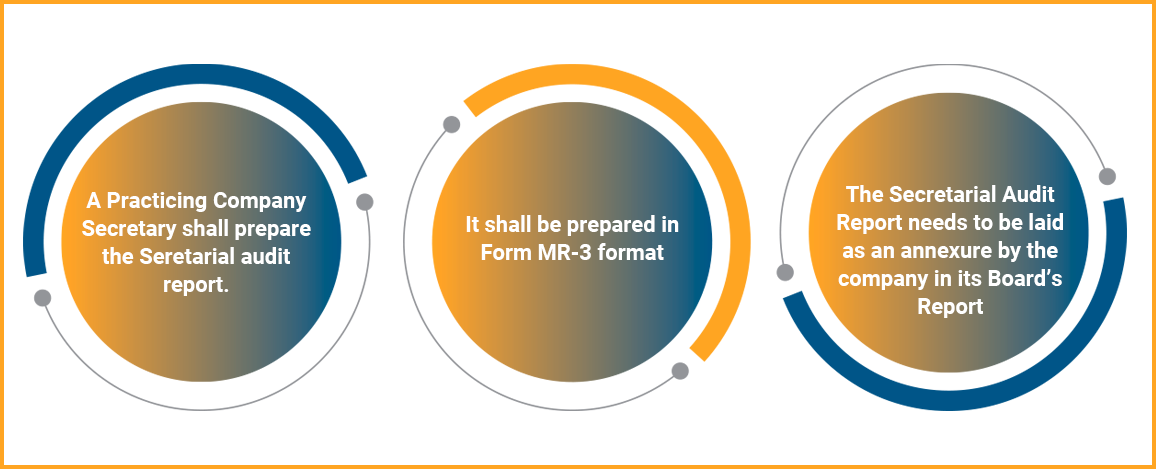
It is a process to check compliance to the provisions of law, rules and regulations, maintenance of books etc. by an independent professional to make sure that the company complies with the legal requirements and procedural needs and also follows the due process. It is a mechanism to monitor compliance with the requirement of stated law.
Objective of secretarial audit
Following are the objectives of secretarial audit-
- To check and report on the competition of compliances according to provision of law.
- To point out the non-compliances.
- To safeguard the interest of the stakeholder that includes customers, employees etc.
- Compliances are to be followed to avoid any unwarranted legal action or penalties.
Applicability of Secretarial audit in India
The mandatory provision regarding applicability of secretarial audit are-
- Every listed company
- Every public company having a paid up share capital of Rs. 50 crore or more and having turnover of Rs. 250 crore or more.
- Company having outstanding loans or borrowing from banks or public financial institutions of Rs. 100 crore or more.
Scope of Secretarial Audit
Scope comprises verification of the compliances under the following-
- Companies Act, 2013 and the rules made there under;
- Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 and the rules made there under;
- Depositories Act of 1996 and the rules made there under;
- Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999
- Regulations and guidelines provided under the Securities and Exchange Board of India, Act 1992;
- Reporting on the compliance of secretarial standards issued by Institute of Company Secretaries of India; and
- Other laws are applicable specifically to the company that means all the laws that are applicable to specific industries.
Appointment of Secretarial auditor
Process of appointment of a secretarial auditor are as follows-
- Firstly, consent of the secretarial auditor is required.
- Thereafter, a certified copy needs to be filed of the resolution passed in the Board meeting with the Registrar of companies in MGT-14.
- Make an appointment of such an auditor in the Board meeting and fix the remuneration in the meeting.
Process of secretarial audit in India
The process are as follows-
- Appointment of secretarial auditor.
- Communication to earlier incumbent
- Primary discussion will take place about the company with secretarial auditor
- After the meeting an audit plan is finalized and the staff is briefed.
- Testing, interview and analysis
- The working papers are prepared
- Audit summary for discussions
- Finally the secretarial audit will be submitted.
Documents required for secretarial audit
Following are the documents which are required for secretarial auditing-
- Charter documents and statutory registers
- Birds and general meeting minutes and notices
- The audited financial statement as well as last year’s secretarial audit report
- Annual performance reports, lease deeds,bonds and return.
- Registers maintained under the labour law
- Details of remuneration and sitting fees paid to directors
- Details of CSR amount
- Details of bank account for dividend
- ECB returns details
Benefits of secretarial audit
- It’s an effective mechanism to ensure the compliance with the procedural and legal requirements;
- It promotes the level of confidence to directors and key managerial personnel etc.
- It ensures that legal and procedural requirements are met that in turn allows the directors to concentrate on crucial business dealings;
- It strengthens the goodwill of the company for their regulators as well for their stakeholders;
- It is also an effective governance and compliance risk management tool;
- It, further, helps an investor in analyzing the compliance level of companies thereby increasing the reputation also;
- It administers professional discipline and also self-regulation;
- It may be an effective due diligence performance for the prospective acquirer of the company or a partner of a joint venture; and
- It helps to detect any non-compliance and helps in taking corrective action.
Conclusion
Secretarial audit in India is independent and it is beneficial for the companies who follow it as it improves their operations. It can help an organization in completing their objectives.